Transgenic Animals Definition Biology

Transgenic animals are specially designed to study the role of genes in the development of certain diseases.
Transgenic animals definition biology. Transgenic animals definition biology. Transgenic animals are also becoming useful commercially. Foreign genes are inserted into the germ line of the animal so it can be transmitted to the progeny.
The term transgenic animal refers to an animal in which there has been a deliberate modification of the genome - the material responsible for inherited characteristics - in contrast to spontaneous mutation FELASA September 1992 revised February 1995. Toxicity testing in such animals will allow us to obtain results in less time. Transgenic plants can be made by introducing foreign DNA into a variety of different tissues.
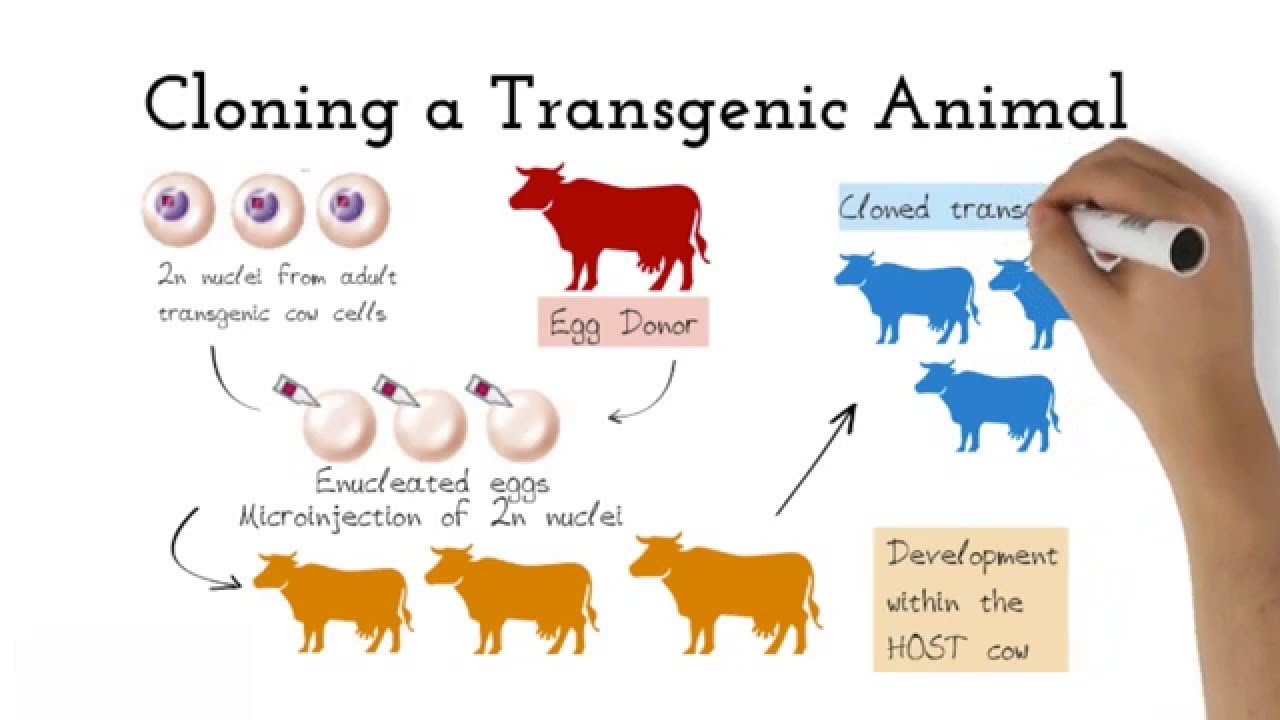
Full article Transgenic Animals The. These transgenic models are used in research for the development of medicines. Sheep goats pigs cows rabbits rats mice fish insects parasites and even humans have previously been used in this modification process.
Transgenesis is the process by which mixing up of genes takes place. Theoretically all living beings can be genetically manipulated. Disease Animal Models - BSRC Alexander FlemingTransgenic Animal Models - Biomedcode.
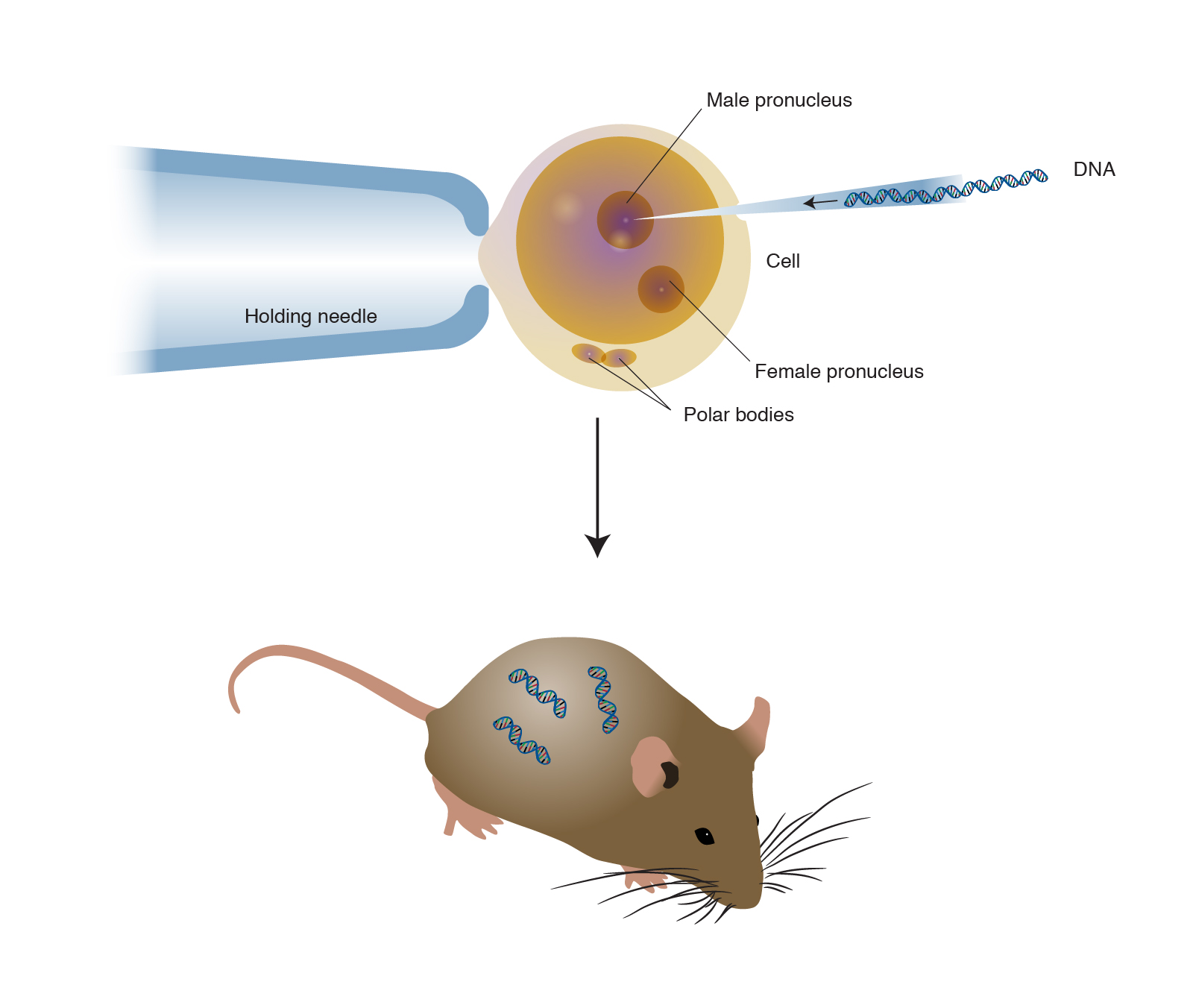
Transgenic Animals Definition Biology. Transgenic animal industrial applications 3 chemical safety testing toxicity-sensitive transgenic animals animal bioreactor protein production. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome.
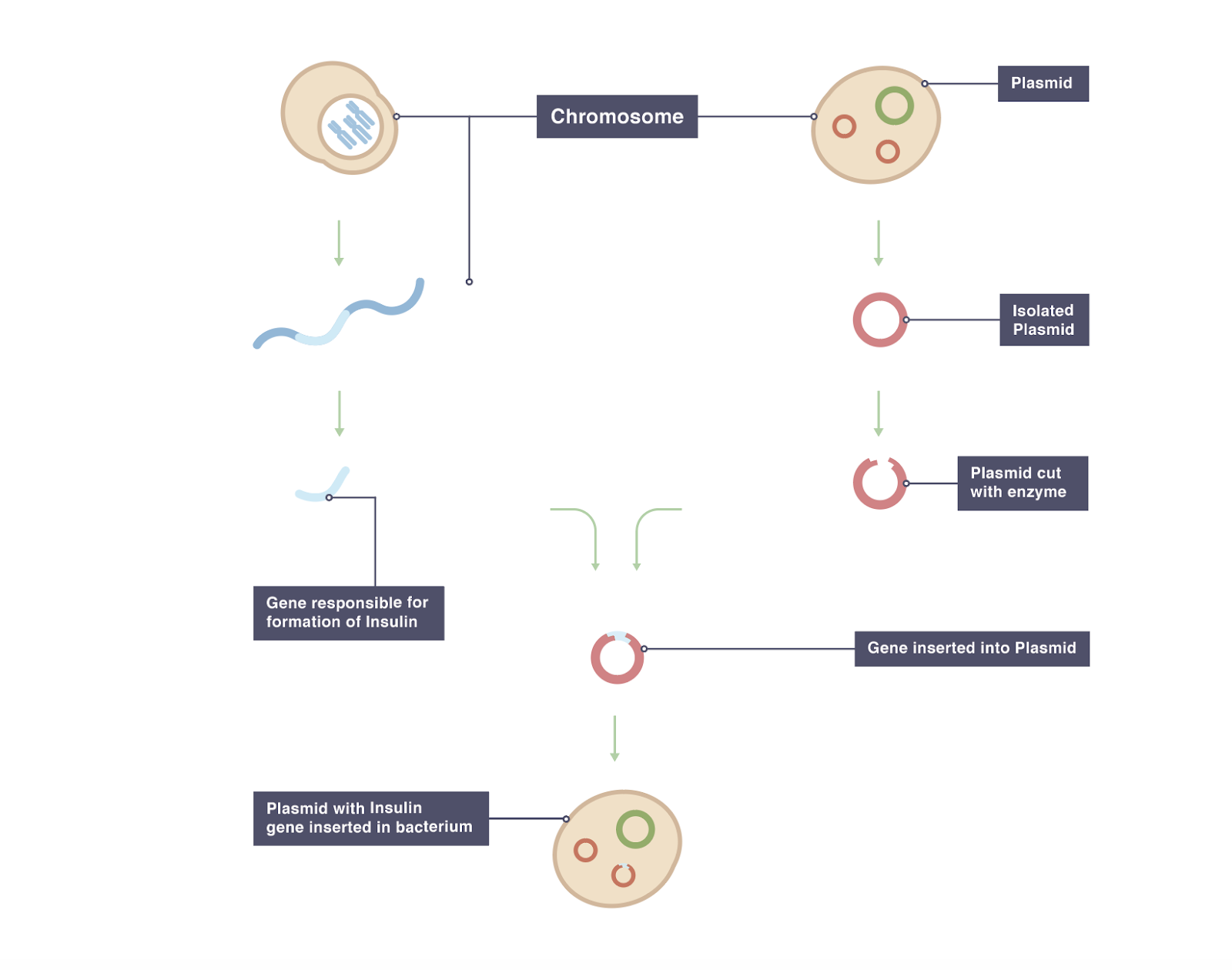
The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. To determine an unknown genes function. Moreover in order to devise a cure for these diseases the transgenic animals are used as model organisms.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)