Food Chain Definition Ecology
The sequence of the transfer of food energy from one organism to another in an ecological community.
Food chain definition ecology. These easy recipes are all you need for making a delicious meal. In ecology a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. The definition of a food chain is a system where a small animal is the food for a larger animal which in turn is the food for an even larger animal.
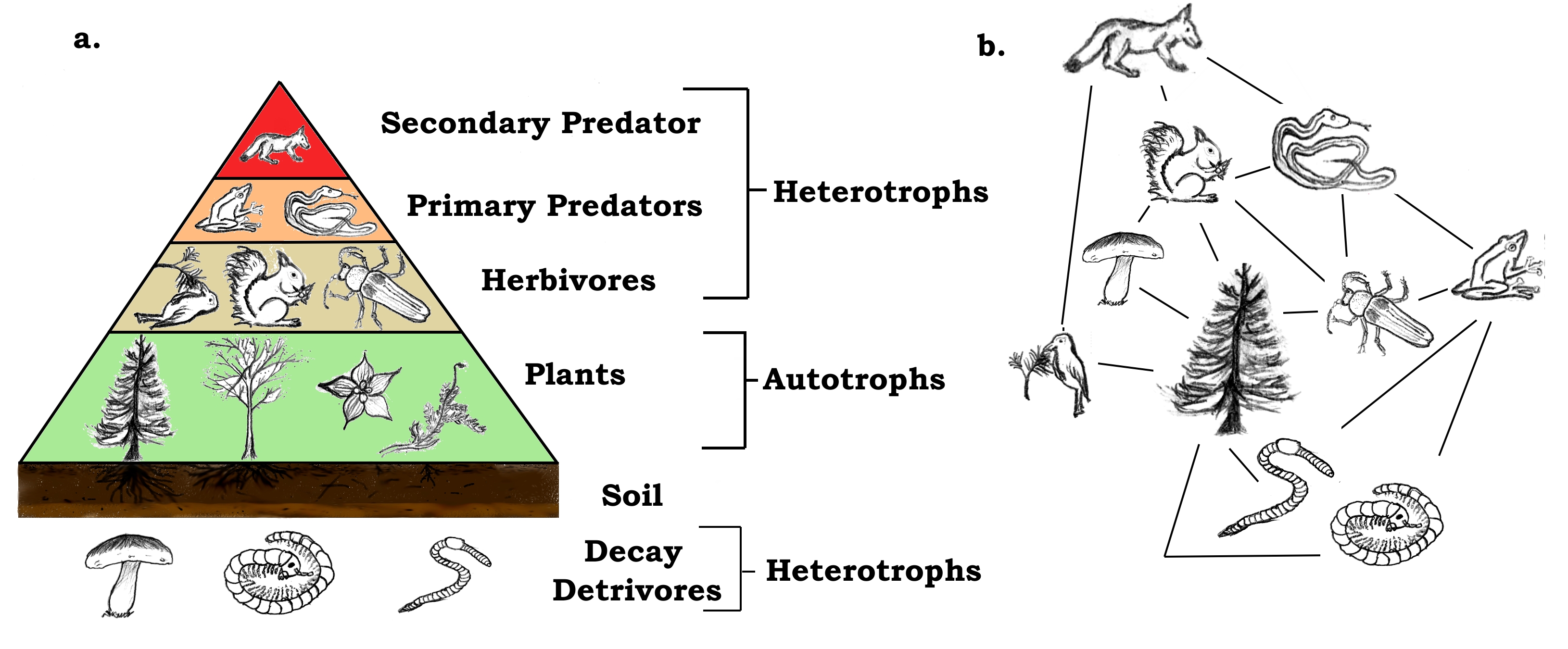
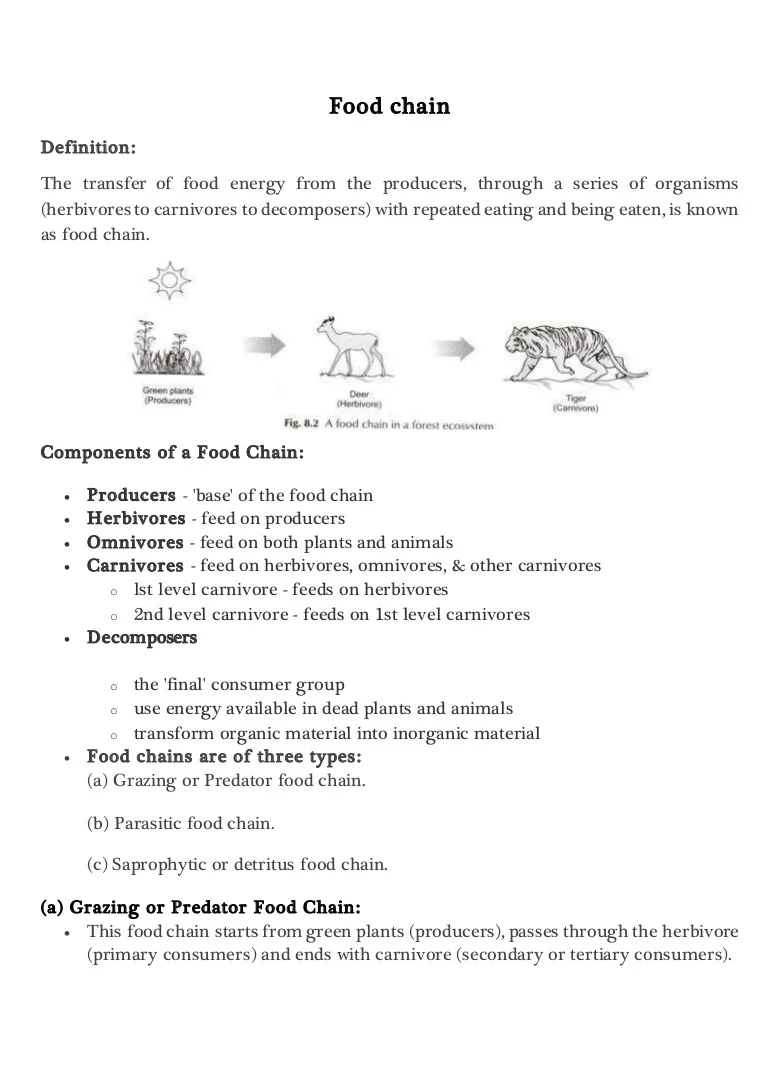
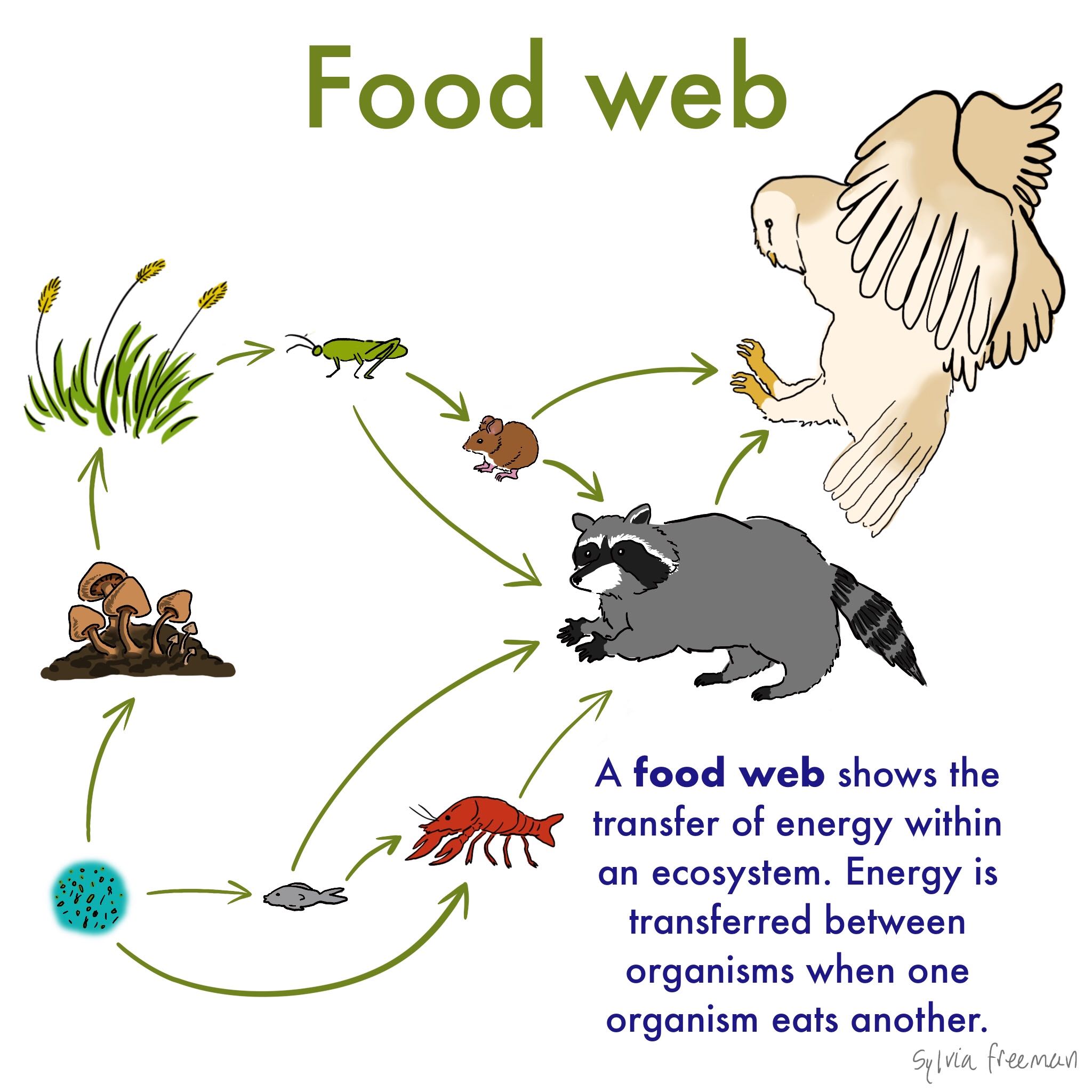
The producers that are capable to produce their own food are called autotrophs. A food web shows multiple food chains multiple relationships and connections. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism.
Carl Linnaeus in an ecologically important essay The Economy of Nature Linnaeus Latin 1749. Depending on producer and different levels of consumers some examples of food chain are given below. Food chain definition ecology Thinking Food Chain Definition Ecology to Eat.
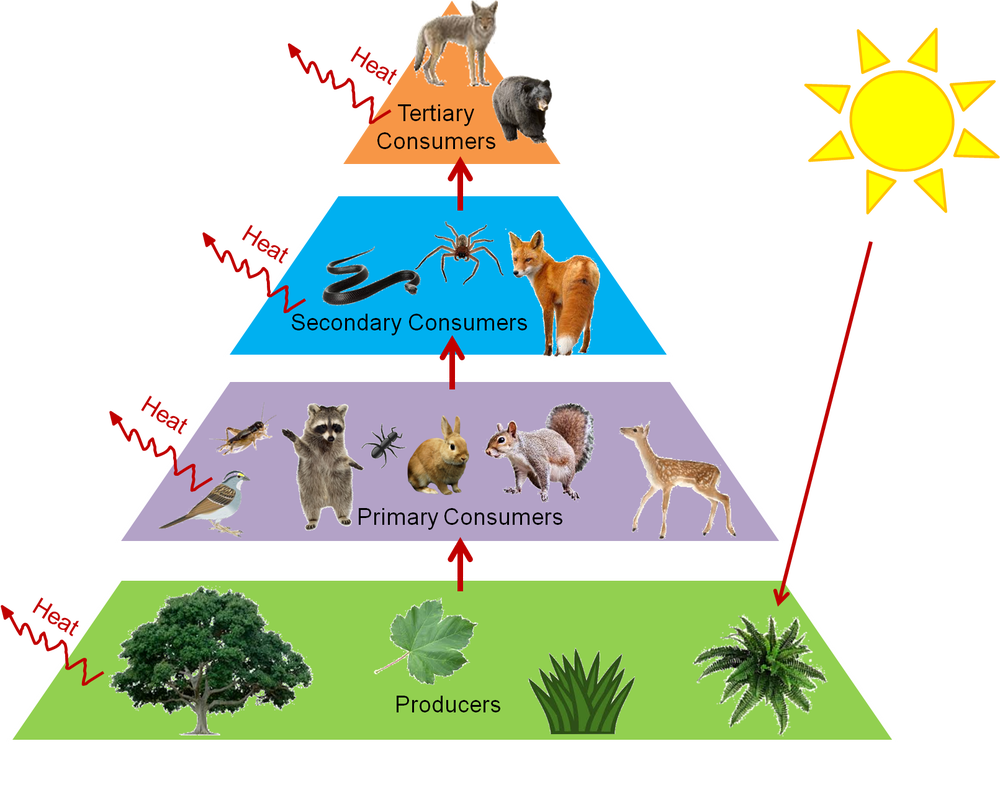
Plants are eaten by insects insects are eaten by frogs the frogs are eaten by fish and fishes are eaten by humans. In 1927 he recognized that the length of these food chains was. Flow of energy in an ecosystem is one way process.
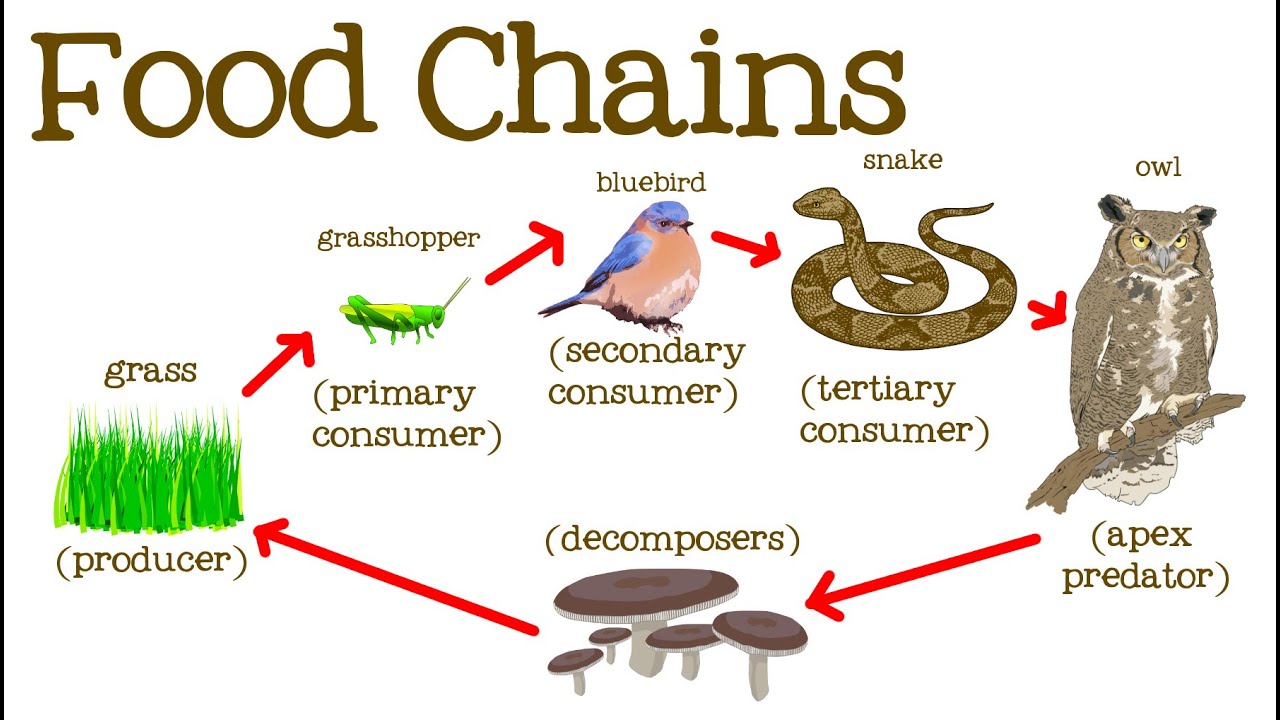
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaa food chain also shows how the organisms. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the Sun to make their food and ending at an apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaA food chain also shows how organisms are. Food chain - ecology a community of organisms where each member is eaten in turn by another member bionomics environmental science ecology - the branch of biology concerned with the relations between organisms and their environment.
In food chain the plants or producers are consumed by only the primary consumers primary consumers are fed by only the secondary consumers and so on. The food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem. A food chain shows what eats what in a particular habitat.